One of the classical features of enterprise IT is complexity. But whether something is complex or not isn’t necessarily a standalone catalyst for change; what matters the most is whether or not systems run the way they should. An Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) architecture can play a vital role in helping businesses handle this complexity.
By leveraging an ESB solution, companies can change the way organizations do business and perform several key functions that assist the developer in application integration.
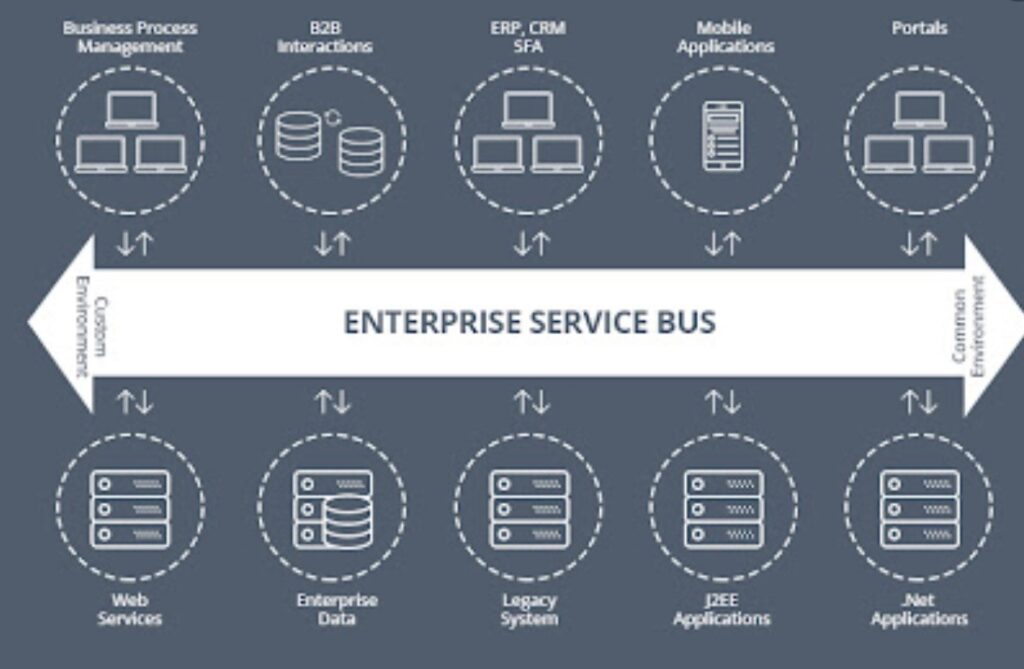
What is an Enterprise Service Bus?
In actuality, an ESB is an approach to IT application integration architecture. An ESB is designed to integrate multiple applications over a “bus-like” infrastructure. It is placed somewhere between the framework and a suite as another way to perform application integration. Being a middleware tool, it helps business users distribute tasks among myriad connected components that make up an application.
A number of tasks can be carried out by this application integration architecture:
- Implement routing
- Execute translation
- Offer the ability to connect to the “bus”
- Render a blanket way for the movement of tasks
- Subscribe to messages sent across systems
- Cater other integration capabilities
How Does an ESB Solution Function?
The primary function of ESBs is to simplify the mess that can arise when different formats, services and applications or mainframes have to be integrated. But, how exactly does it work?
- An ESB application architecture such as from Adeptia comprises a set of switches that help companies send a direct message on a specific route between either the application and/or components.
- Each enterprise encompasses a specific business policy in place that determines which path the ESB will take these messages.
Anything that’s connected to an ESB cannot communicate directly with one another as the communication happens via the ESB. Simply put, the same ESB exposes the same service interface to potential clients to speed up operations and processes.
One of the most important benefits offered by ESB is it offers a single point of access. As users connect clients and services via an ESB, they have to look for services in one, single location, the ESB. All that’s needed to be done is to reconfigure ESB, and the company can still access the service via the ESB.
Additionally, ESB function like a transaction manager. That means it help users coordinate distributed transactions across the business ecosystems. Suffice to say, organizations can leverage an ESB solution to drive transactions – easily and rapidly.
An Enterprise Service Bus also play a role of a security manager. Not only can it manage security but also centralize processes like authentication and authorization.
ESB also function as a service proxy. In doing so, it acts as a gateway for applications that aren’t exposed to a standardized service interface. For example, if an application uses a Java RMI service and the rest of all applications run on .NET, making a call to the RMI service directly is not possible. With the aid of an ESB, a company can easily implement a service proxy in Java which can call an RMI service. Hence, communications become easier and smoother.

How Can an ESB Solution Help a Business Perform Operations?
An ESB solution has a number of use cases. It’s time to take a deeper look at how an enterprise can take savor the benefits of an ESB. Here are some functionalities provisioned by an ESB:
Decoupling
ESB application architecture enables users to decouple clients from service providers.
Message Enhancement
With the help of an ESB, a user can isolate a client while making some general changes to the message at the same time.
Transport Protocol Conversion
It allows business users to accept one input protocol and establish communication with a different service provider, even if the service provider is on a separate protocol.
Message Transformation
A user can rely on ESBs to transform any potential incoming messages into outgoing formats and structures.

Take Your Business to New Heights
An ESB can help businesses navigate through the complexity and enable business users to connect data and applications without delay. Along with that, it facilitates service location transparency, sharing of services and processes across an enterprise, and separation of business service from the service implementation. Not only can that optimize processes but also help companies deliver the promised value to customers.









