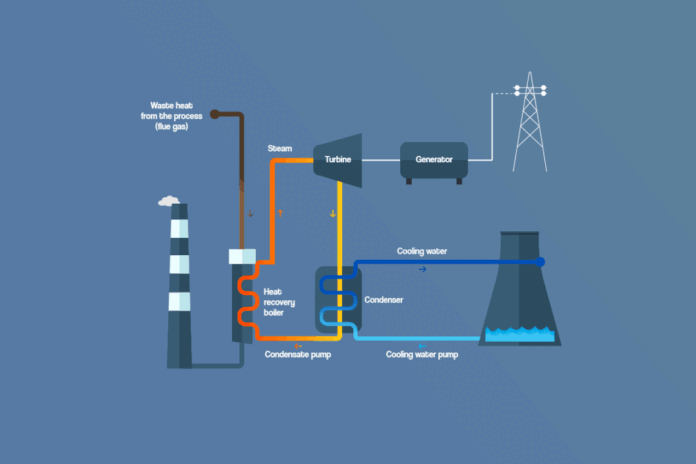
In a world where sustainability is paramount, the concept of turning waste into watts through Heat Recovery Systems is gaining traction. The innovative heat recovery ventilation system can convert wasted heat into a valuable energy source, contributing to cost savings and environmental conservation.
From industrial applications to residential heating, heat recovery systems are revolutionising how we think about energy efficiency and environmental impact.
Let’s explore the power of heat recovery systems, which transform waste into watts, and how they’re heating up the energy sector.

The Power of Waste Heat Recovery
The efficiency of generating power from waste heat recovery is heavily dependent on the temperature of the waste heat source. In general, economically feasible power generation from waste heat has been limited primarily to medium- to high-temperature waste heat sources (i.e., greater than 500 °F).
Between 20 and 50 per cent of industrial energy input is estimated to be lost as waste heat. This wasted energy, often from hot exhaust gases, cooling water, and heat lost from hot equipment surfaces, significantly contributes to energy inefficiency. However, with heat recovery systems, this waste heat can be harnessed and converted into usable energy, thereby improving energy efficiency and reducing environmental impact.
Implementing heat recovery systems can recover a significant portion of this otherwise lost energy, potentially reducing overall energy consumption by 10-30%.
Waste-to-energy plants, for instance, burn municipal solid waste (MSW) to produce steam, which is then used to power an electric generator turbine. In the United States, about 85 pounds of MSW can be burned as fuel to generate electricity for every 100 pounds of MSW. This process reduces the volume of waste by about 87% and generates valuable energy.
Types of Heat Recovery Units
Waste heat recovery systems come in various types, each designed to capture and repurpose waste heat from different sources and processes. Here are some of the different types of waste heat recovery systems:
- Recuperators are heat exchangers where exhaust gases are passed through metal tubes carrying the inlet gas, preheating it before entering the process.
- Regenerators: These systems reuse the same stream after processing. The heat is regenerated and reused in the process.
- Heat Pipe Exchanger: Heat pipes are excellent thermal conductors. They are used in renewable energy technology in evacuated tube collectors.
- Thermal Wheel or Rotary Heat Exchanger: This involves a rotating circular honeycomb matrix of heat-absorbing material within the supply and exhaust air streams.
- Economiser: In this case, waste heat in the exhaust gas is passed along a recuperator that carries the inlet fluid for the boiler, thereby reducing thermal energy intake.
- Heat Pumps: These use an organic fluid that boils at a low temperature, enabling the regeneration of energy from waste fluids.

Advantages of Heat Recovery Systems
Heat recovery systems offer numerous benefits for the environment, businesses, and homeowners. They also help to reduce humidity and condensation, which can cause health problems and affect walls and structures over time.
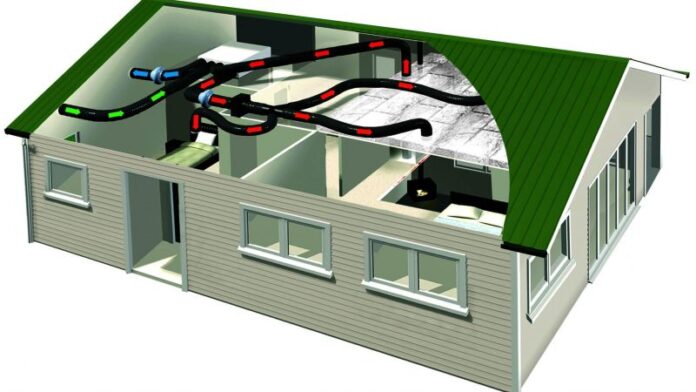
In residential and commercial buildings, heat recovery ventilation (HRV) systems maintain a comfortable indoor environment while improving energy efficiency. These systems recover about 60–95% of the heat in the exhaust air, significantly improving the energy efficiency of buildings. They also help improve indoor air quality, prevent mould and condensation, and balance heat distribution throughout the building.
- Energy Efficiency: By recovering and reusing waste heat, these systems enhance the overall efficiency of industrial processes.
- Cost Savings: They significantly reduce energy consumption and operational costs.
- Reduced Pollution: These systems lower thermal and air pollution, as less flue gas is emitted due to energy recycling.
Heat recovery systems can be even more beneficial for businesses as they produce and use more energy. Many technologies that recover lost heat in large factories and industrial plants are now available, significantly reducing energy loss through emissions.
Challenges and Opportunities: Navigating Complexity
While the potential benefits of heat recovery systems are undeniable, challenges exist in implementing these technologies on a broader scale. The upfront costs of installing such systems can be a deterrent for some industries despite the long-term savings and environmental benefits.
These include the quality and quantity of the waste heat source, the technical and economic feasibility of the recovery system, and regulatory and institutional barriers. However, technological advancements and a growing focus on sustainability drive the development of more efficient and cost-effective heat recovery solutions.
the use of heat recovery systems is expected to increase. Continuous innovations are being made to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of these systems. For example, wood-burning stoves that can charge your phone and systems that can generate electricity from heat at a cement kiln are just a few examples of how heat can be creatively utilized.
Striking a balance between economic feasibility and ecological responsibility remains a key challenge for businesses considering heat recovery solutions.
The Path Forward: A Call to Action
A heat recovery system is the preferred option as buildings become more efficient at heat retention and energy consumption. Heat recovery is one of the significant issues for the sustainable energy industry, making the most of what we produce and creating more efficient heating systems from the home to the heart of our homes, offices, and factories.
The choice is clear as we stand at the crossroads of technological innovation and environmental consciousness. Heat recovery systems represent a tangible, impactful solution to the dual challenges of energy efficiency and climate change.
Looking ahead, the potential of heat recovery systems is undeniable. As the world continues to grapple with climate change and energy insecurity challenges, these systems offer a promising solution. By harnessing the power of waste heat, we can improve energy efficiency and contribute to a greener and more sustainable future.
As we harness the latent energy within our waste, we generate watts and cultivate a legacy of responsible stewardship for generations to come. The journey from waste to watts is a narrative of transformation, and it’s a story we all have the power to write.