In today’s data-driven world, information is power. Organizations across industries are constantly seeking ways to harness data effectively and gain valuable insights to drive their decision-making processes. This is where Geographic Information Systems (GIS) mapping software comes into play, revolutionizing the way data is visualized and analyzed. GIS software enables the integration of various data sets onto a single interactive map, providing a comprehensive view of spatial relationships and patterns.
With the advent of GIS mapping software, organizations can unlock the full potential of their data by visualizing it in a geographic context. This technology allows users to layer different types of information onto a map, such as demographic data, land use patterns, infrastructure networks, and environmental factors. The ability to overlay and analyze multiple data sets simultaneously provides a deeper understanding of complex relationships, facilitating better decision-making processes when choosing the right software with these pointers https://mappitall.com/blog/how-to-choose-best-gis-software.
Enhancing Decision-Making with Geographic Information Systems
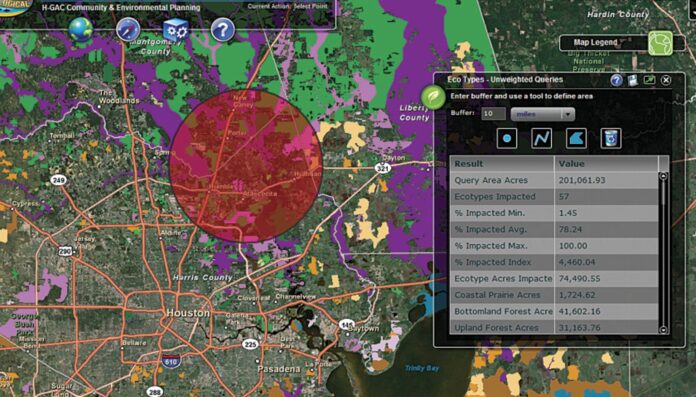
One of the key advantages of GIS software is its ability to perform spatial analysis. This allows businesses to evaluate the proximity of resources, identify potential risks, and optimize their operations. For example, in retail, GIS mapping software can analyze customer demographics and purchasing patterns to determine the optimal location for a new store. Similarly, in logistics, GIS can optimize delivery routes by considering factors such as traffic patterns, road conditions, and customer locations.
Furthermore, the best GIS software enables organizations to perform scenario analysis and predictive modeling. By simulating different scenarios and evaluating their potential outcomes, decision-makers can make more informed choices. For instance, urban planners can use GIS mapping software to simulate the impact of different development plans on traffic flow, population density, and environmental factors. This empowers them to make data-driven decisions that lead to sustainable and efficient urban development.
Leveraging GIS Mapping for Efficient Resource Management
Efficient resource management is a critical aspect of any organization’s success, whether it is managing infrastructure, utilities, or natural resources. Geographic Information Systems mapping software provides powerful tools for resource management by integrating spatial data and enabling organizations to optimize their resource allocation and utilization.
It allows organizations to visualize and analyze their resources in a geographic context, providing valuable insights for effective resource management. For example, utility companies can utilize GIS software to map their network infrastructure, such as power lines and substations, and monitor their performance in real time. This enables them to identify potential issues, optimize maintenance schedules, and respond quickly to outages, ensuring reliable service delivery.
Transforming Urban Planning and Infrastructure Development through GIS

Urban planning and infrastructure development are complex processes that require a comprehensive understanding of spatial relationships, land use patterns, and demographic factors. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) mapping software has emerged as a transformative tool in urban planning, enabling city planners and policymakers to make informed decisions and create sustainable urban environments.
GIS mapping software allows urban planners to integrate diverse datasets, such as transportation networks, land use patterns, population density, and environmental factors, onto a single map. This holistic view of spatial relationships enables planners to identify opportunities for efficient land use, improve transportation networks, and enhance environmental sustainability. By visualizing data in a geographic context, city planners can gain valuable insights and make informed decisions that shape the future of their cities.
Furthermore, GIS software facilitates effective community engagement and participation in the urban planning process. By creating interactive maps and visualizations, city planners can communicate their ideas more effectively to the public and gather feedback. This participatory approach fosters collaboration and transparency, ensuring that the final urban development plans reflect the needs and aspirations of the community.
Unlocking the Potential of GIS in Environmental Conservation and Natural Resource Management
GIS mapping software allows organizations to analyze and visualize environmental data in a geographic context, providing valuable insights for conservation efforts. For example, by overlaying habitat maps, biodiversity records, and land use data, conservation organizations can identify areas of high ecological significance and prioritize their conservation efforts. This enables targeted and efficient resource allocation, ensuring the long-term protection of critical ecosystems.
Furthermore, GIS systems software plays a crucial role in monitoring and managing natural resources. By integrating data on land use, water availability, and climate patterns, organizations can assess the health and sustainability of natural resource systems. For instance, forestry departments can use GIS mapping software to monitor forest cover, identify areas at risk of deforestation, and plan conservation strategies accordingly. Similarly, fisheries management agencies can utilize GIS to track fish populations, identify overfished areas, and implement sustainable fishing practices.
GIS Mapping in Agriculture: Precision Farming and Sustainable Practices

Agriculture plays a vital role in ensuring food security and supporting rural economies. GIS mapping software allows farmers to create detailed maps of their fields, capturing information on soil properties, nutrient levels, and moisture content. By analyzing these data layers, farmers can identify variations within their fields and tailor their farming practices accordingly. For example, they can adjust irrigation levels based on soil moisture patterns, apply fertilizers more precisely, and optimize crop planting to maximize yield.
Moreover, agriculture GIS software enables farmers to monitor and manage their crops more efficiently. By integrating real-time weather data, satellite imagery, and sensor data from farm equipment, farmers can track the growth and health of their crops in real-time. This allows for early detection of pests, diseases, or nutrient deficiencies, enabling prompt interventions and minimizing crop losses. Additionally, by analyzing historical data, farmers can identify trends and patterns, improving their long-term planning and decision-making processes.
Improving Emergency Response and Disaster Management
By integrating data on weather conditions, population density, infrastructure networks, and evacuation routes, emergency responders can identify areas at risk, plan evacuation strategies, and allocate resources accordingly. This real-time visualization of data on interactive maps enables more informed and coordinated decision-making, enhancing the effectiveness of emergency response efforts.
Furthermore, GIS mapping software enables organizations to analyze the potential impact of natural disasters and simulate different scenarios. By analyzing historical data, topographic information, and population density, disaster management agencies can model and predict the consequences of natural hazards. This helps in developing proactive strategies, implementing preventive measures, and reducing the vulnerability of communities to future disasters.
GIS Mapping in Transportation: Optimizing Routes and Enhancing Mobility

Efficient transportation systems are crucial for economic growth, mobility, and quality of life. Geographic Information Systems mapping software has transformed the transportation industry by enabling organizations to optimize routes, manage traffic, and enhance overall mobility.
It allows transportation agencies to analyze various spatial data, including road networks, traffic patterns, and demographic information, to optimize route planning. By considering factors such as distance, traffic congestion, and travel time, GIS software can generate the most efficient routes for vehicles. This not only reduces travel time and fuel consumption but also minimizes congestion and enhances the overall flow of traffic.









